SustainIQ Institutional Knowledge Assessment Report
Universitas Diponegoro (UNDIP), 2025
1. Introduction
SustainIQ is an internal self-assessment tool designed to measure sustainability literacy and awareness across all stakeholders within Universitas Diponegoro (UNDIP). The assessment captures how deeply members of the UNDIP academic community—students, lecturers, and administrative staff—understand sustainability concepts, the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and the principles of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) responsibility.
The 2025 SustainIQ assessment builds on UNDIP’s long-standing commitment to the SDGs, as mandated by the Rector’s Circular Letter on SDG Implementation (No./UN7.P/SE/2020). This year’s survey sought to quantify knowledge levels and identify learning gaps, providing evidence for continuous improvement of the university-wide sustainability initiatives. A total of 17923 respondents participated in the evaluation from across faculties and administrative units, representing an inclusive snapshot of the university community.
2. Statistical Overview
The SustainIQ dataset revealed that UNDIP’s community maintains a high level of sustainability awareness. The average knowledge score was 14.64 out of 20, equivalent to 73.2 percent accuracy. Scores ranged from a minimum of 2 to a maximum of 20, with a standard deviation of 4.12, suggesting moderate variation among respondents.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Respondents | 17923 |
| Average Score | 14.64 / 20 |
| Highest Score | 20 |
| Lowest Score | 2 |
| Standard Deviation | 4.12 |
This statistical spread indicates that most respondents possess strong conceptual understanding, while a smaller portion—particularly among administrative staff—show limited exposure to structured sustainability knowledge
3. Performance by Participant Group
Breaking down the results by category yields meaningful insights into how sustainability literacy differs across roles within UNDIP.
| Category | Respondents | Average Score | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lecturers (Dosen) | 4022 | 15.87 | 3.43 |
| Students (Mahasiswa) | 7344 | 14.95 | 4.18 |
| Staff (Tendik) | 6557 | 13.53 | 4.20 |
Lecturers recorded the highest average score, reflecting their familiarity with SDG-related research, teaching integration, and academic discourse. Students performed well, demonstrating that sustainability topics are effectively embedded in coursework but still leave room for more practical, experiential learning. Administrative staff scored slightly lower, revealing the need for targeted training programs on sustainability practices within operational and support functions.
4. Data Visualization
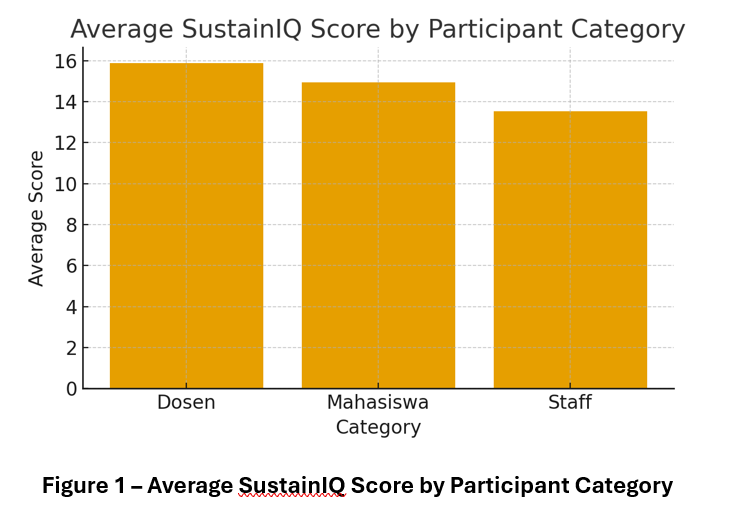
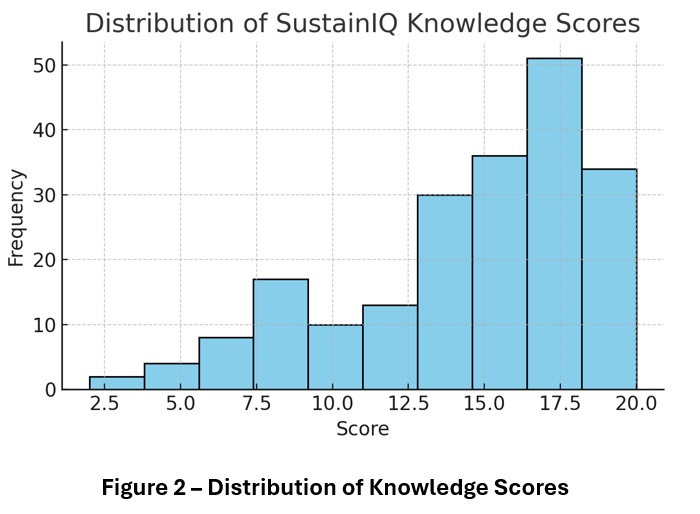
The bar chart highlights that lecturers lead in sustainability understanding, while staff lag behind, suggesting that sustainability knowledge remains concentrated among academic personnel. The histogram shows a slightly right-skewed distribution: most participants scored between 12 and 18, confirming a generally strong sustainability knowledge base but also highlighting that full mastery (scores > 18) is achieved by only a subset of respondents.
5. Interpretation and Insights
Overall, the SustainIQ results confirm that UNDIP’s community demonstrates a mature and integrated awareness of sustainability principles. The institution’s continuous efforts—such as embedding SDGs in 98 percent of its courses, promoting multidisciplinary environmental research, and launching the School of Sustainability—are reflected in these positive outcomes.
Lecturers exhibit the strongest conceptual foundation, likely due to ongoing exposure to international research collaborations, the SDGs Center’s academic forums, and direct involvement in curriculum development.
Students benefit from sustainability-oriented subjects and project-based learning through Kuliah Kerja Nyata (KKN) and community engagement activities, which cultivate applied sustainability literacy.
Administrative staff, while showing enthusiasm, require more structured training opportunities to connect sustainability principles with daily campus operations, procurement, and energy-efficiency practices.
6. Thematic Strengths and Gaps
Strengths
- Strong awareness of SDG 13 (Climate Action), SDG 14 (Life Below Water), and SDG 15 (Life on Land) across respondents.
- Institutional culture that links sustainability with UNDIP’s scientific core of Coastal, Tropical, and Marine Resources.
- Positive correlation between academic rank and sustainability literacy, reflecting effective faculty engagement.
Gaps
- Uneven knowledge of SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) and SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals).
- Need for greater operational understanding among staff (e.g., waste management, carbon tracking, sustainable procurement).
- Limited cross-functional collaboration in applied sustainability projects.
7. Implications for UNDIP’s Educational Strategy
The findings suggest that UNDIP is well-positioned to consolidate its leadership as a sustainability-driven institution. Integrating sustainability knowledge into all levels of education has yielded tangible learning outcomes, yet the data also highlight the need to broaden sustainability literacy beyond classrooms.
Future strategies should emphasize interdisciplinary teaching methods, micro-credentials, and continuing-education programs tailored for administrative personnel. Embedding sustainability performance indicators into annual faculty evaluations and operational targets could further ensure institutional coherence and accountability
8. Recommendations for Future Development
| Focus Area | Key Action | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Staff Capacity Building | Launch mandatory training on SDG implementation for all administrative units | Higher operational literacy and alignment with green campus goals |
| Student Learning Experience | Integrate gamified SustainIQ modules and case-based projects | Stronger applied understanding and innovation skills |
| Cross-Faculty Synergy | Develop joint courses and research across faculties | More interdisciplinary solutions to sustainability challenges |
| Community Outreach | Expand School of Sustainability programs to local stakeholders | Broader impact on regional SDG achievement |
| Continuous Monitoring | Conduct SustainIQ annually and track progress | Longitudinal data to inform strategic planning |
9. Conclusion
The 2025 SustainIQ results affirm that Universitas Diponegoro has built a robust culture of sustainability knowledge and awareness. With an average performance of 73 percent and near-universal participation across stakeholder groups, UNDIP demonstrates that sustainability education is not only integrated into academic programs but also embedded in its institutional ethos.
To further advance, the university should expand sustainability learning opportunities for all personnel, ensure continued evaluation through annual SustainIQ cycles, and leverage the insights to refine UNDIP’s role as a regional model for sustainable higher education.
